2024/12/16
Part 1: What is an Electric Linear Actuator? Definition & Types Explained
News and Articles
Electric linear actuators play a vital role in modern machinery, offering a reliable solution for converting electrical energy into linear motion. These versatile devices power applications ranging from industrial automation to home appliances. In this white paper series, we’ll dive into the fundamentals of electric linear actuators, their working principles, types, and how to select the right actuator for specific applications.
What is an Electric Linear Actuator?
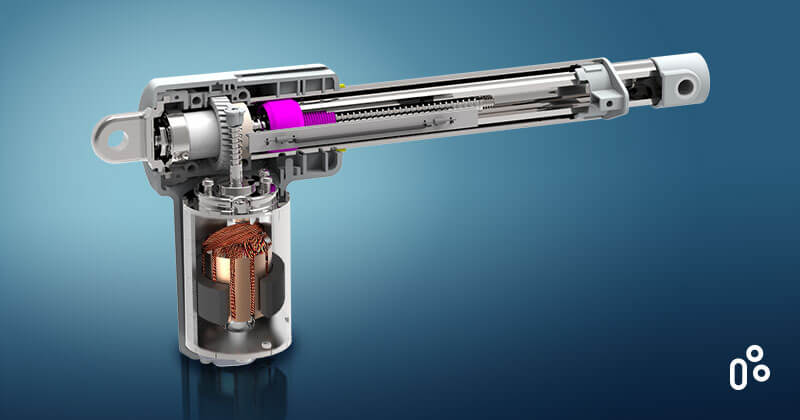
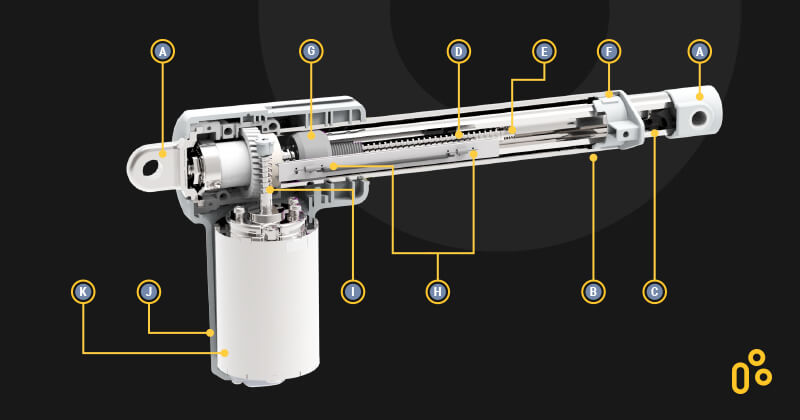
An electric linear actuator is an electromechanical device mainly composed of a motor, a set of gears, and a motion mechanism consisting of a worm and tube. It converts the motor’s rotary motion into linear motion by driving the gears and worm gear.
Unlike rotary actuators, which create rotational movement, electric linear actuators are designed to move objects along a straight line. They are commonly used in applications that require precise positioning, such as lifting, lowering, pushing, or pulling loads.
If you want to know more about the components of an electric actuator, please read our following white paper series.
How Do Electric Linear Actuators Work?
The core mechanism of an electric linear actuator includes a motor (often DC or AC), a lead screw, and a nut. As the motor rotates, it drives the lead screw, causing the nut to move along the screw’s axis. This movement translates into linear motion, which is used to perform tasks such as opening windows, adjusting hospital beds, or automating industrial processes.
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how they work:
- Power Input: The actuator receives electrical energy from a power source, such as a battery or direct electrical supply.
- Motor Activation: The motor begins rotating, generating torque.
- Screw Mechanism: The motor’s rotation drives a threaded lead screw, which moves a nut attached to the load.
- Linear Motion: The nut’s movement creates linear motion, allowing the actuator to push, pull, or lift the load.
Modern electric linear actuators often include advanced features like position sensors, limit switches, and feedback systems for greater control and precision. This makes them suitable for high-precision tasks in industries such as robotics and medical equipment.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Electric Linear Actuators?
-
Advantages:
- Precision and Control: Electric linear actuators provide accurate and repeatable positioning, ideal for automation tasks.
- Energy Efficiency: They consume less power than hydraulic or pneumatic actuators, particularly in static hold applications.
- Low Maintenance: With fewer moving parts and no fluid systems, they require minimal upkeep.
- Versatility: They can operate in various environments and are easily programmable for complex movements.
- Quiet Operation: Compared to hydraulic and pneumatic systems, electric actuators operate more quietly.
-
Disadvantages:
- Force Limitations: Electric actuators produce less force compared to hydraulic systems, limiting their use in heavy-duty applications.
- Dependency on Power Supply: A consistent power source is essential, which may not be ideal for all settings.
What Are the Different Types of Electric Linear Actuators?
Electric linear actuators come in various types to meet diverse application needs. Linear actuators, lifting columns, gear motors, and others all have their unique features and strengths. Discover below the list of the different types of actuators and adapt to the needs of equipment manufacturers.
1. Parallel Electric Actuators
The motor is parallel to the worm gear. Parallel electric linear actuators are usually driven by spur gears, which offer a wider range of gear ratios. These actuators allow for a greater range of loads and speeds but aren’t as quiet as actuators with worm gearing.
2. Right Angle or "L" Shaped Electric Actuators
The motor is placed perpendicular to the worm gear. A worm gear usually drives L-shaped electric linear actuators. These actuators offer fewer gear ratio choices than spur gear motors but are quieter and offer increased irreversible force.
3. In-line Electric Actuators
The motor is in line with the worm gear. In-line electric linear actuators, therefore, have a longer retracted length. They are usually driven by a set of planetary gears and are specifically designed to fit into tight spaces. However, they have a higher noise level.
4. Dual Engines
Dual motors operate in two different directions, independently or simultaneously. They are usually driven by gears with a worm wheel and, therefore, offer a quieter movement.
5. Electric Sliding Actuators
Electric slide actuators allow linear movement without the use of an outer tube. The front attachment is linked to the nut, which moves along the worm gear.
Discover our entire range of electric linear actuators.
6. Geared Motors
Gear motors allow the design of economic and versatile systems when combined with one or more worms. Compact, they are usually driven by gears with a worm wheel and are an ideal choice for achieving mechanical synchronization.
Discover our entire range of gear motors.
7. Variable Height Electric Lifting Columns
We manufacture lifting columns for industrial, medical, and ergonomic applications. They allow the vertical movement of high loads while maintaining a high level of stability. Our industrial and medical columns are designed for applications such as medical beds, bariatric beds, or industrial workstations with adjustable heights. Thus, they preserve the safety and comfort of all users.
We also offer a range of ergonomic columns that comply with the BIFMA standard for variable-height offices. This range offers different colors, shapes, orientations, and a 2 or 3-stage design.
Discover our entire range of electrical lifting columns.
What Applications Are Electric Linear Actuators Used For?
Electric linear actuators are incredibly versatile and are used across a wide range of industries and applications, including:
- Home Automation: They power smart furniture, automated windows, and adjustable beds, offering enhanced comfort and convenience for everyday living.
- Medical Equipment: Found in hospital beds, patient lifts, and surgical tables, they provide precise positioning and improve patient care in healthcare environments.
- Industrial Automation: Electric actuators are essential for driving robotic arms, conveyor belts, and assembly lines, ensuring efficiency and accuracy in manufacturing processes.
- Automotive: Used in vehicle seats, tailgates, and other adjustable components, they enhance comfort and functionality for drivers and passengers.
- Workplace Ergonomics: Integral to height-adjustable desks and sit-stand workstations, they promote better posture, reduce the health risks of prolonged sitting, and create a more productive work environment.
The adaptability of electric linear actuators makes them indispensable in any setting where precision, reliability, and automation are critical. Their ability to improve functionality and optimize processes ensures they remain a top choice across industries.
How to Choose an Electric Linear Actuator?
Selecting the correct electric linear actuator is crucial for the success of any electrical equipment development project. Actuators suit a wide range of applications, but each project has its unique requirements. To identify the most suitable electric linear actuator, consider several critical factors: the speed of operation, load capacity, duty cycle, spatial constraints, and the operating environment.
-
Define Your Application Goals
- Load Requirements: Determine the maximum load the actuator must move. This factor is crucial as it affects the actuator's efficiency and lifespan. Ensure the chosen actuator can handle the load without overstraining its capacity.
- Speed: Consider how fast the actuator needs to move to meet your application requirements. Speed affects an actuator's control and precision, especially in time-sensitive applications.
- Duty Cycle: Consider the duty cycle, which is the ratio of active time to rest time. Ensure the actuator can handle the frequency of operation required by your application without overheating or wearing out prematurely.
- Accuracy and Precision: Evaluate the precision level required in the actuator’s movements. High precision is essential in applications like robotics and aerospace, where even minor deviations can be critical.
-
Analyze Operating Environment:
- Environment: Assess the environmental conditions the actuator will be exposed to, such as temperature, moisture, dust, and potential corrosive elements. This assessment will help determine the need for additional features like waterproofing or corrosion-resistant materials.
- Space and Mounting Options: Consider installation dimensions and ensure the actuator fits within your system’s layout. Compact designs, like inline electric actuators, are ideal for space-constrained setups.
With more than 15 years of experience in the manufacturing of electric actuation devices, TiMOTION supports equipment manufacturers from all sectors in their product development projects. Industry, medical, domestic, or professional furniture, we manufacture complete solutions and customize our devices to the specific needs of our customers.
Want to learn more about electric linear actuators? Contact a local sales representative
Frequently Ask Questions (FAQ)
Q1. How do I maintain an electric linear actuator?
A: Electric actuators require minimal maintenance. Regularly check for wear on mechanical components, ensure proper lubrication (if applicable), and keep the electrical connections clean and secure.
Q2. What are the examples of an electric linear actuator?
Actuators find versatile applications across numerous fields, enhancing functionality and automation.
- At home automation, they adjust comfort beds and kitchen extractor hoods.
- Healthcare benefits from actuators in medical care bedding, hospital beds, medical chairs, and patient lifts, facilitating patient care and mobility.
- Ergonomically, they enable adjustments in height for desks and assist in media setups through screen and TV lifts.
- In industry fields, actuators are crucial in agriculture, operating machinery like combine harvesters, sprayers, and tractors, and controlling ventilation systems and solar shading systems, including pergolas and sun shading louvers, optimizing environmental conditions and energy use.
Q3. Are electric actuators energy-efficient?
A: Yes, electric actuators are highly energy-efficient, particularly in applications requiring static hold, as they consume no power when maintaining a position.
Q4. Can electric actuators be used in outdoor environments?
A: Yes, with proper sealing and materials, electric actuators can operate in outdoor conditions. Look for actuators with an IP rating suitable for your application.
→Read more about IP Rating of Linear Actuators
Q5. What safety features are included in electric actuators?
A: Many electric actuators come with built-in limit switches, overload protection, and position sensors to enhance safety and precision.
→Read more about the safety feature options within an electric actuation system